Smart Services: When products turn into services

Smart services such as car sharing, or package tracking form a central foundation for future digital business models. Companies that know how to innovatively exploit the potential of data open up completely new business opportunities.
In this article
Smart Services: When the physical meets the digital world
Service is the magic word of digital transformation. In principle, it means that physical products are converted into services and products are ultimately replaced. There are plenty of examples: conventional hardware and software are transformed into cloud-based services such as Infrastructure as a Service or Software as a Service. The physical car is replaced by car sharing services. Even manufacturers of drills like Hilti now offer their product as a service.
However, Smart Services go beyond pure as-a-service economics. They enable customized services based on Smart Products tailored to the user. As a reminder: Smart Products are Internet-capable products equipped with sensors – such as networked cars, houses, or printers. The data generated and collected by these smart products forms the basis of Smart Services.
To turn a Smart Product into a Smart Service, the raw data collected by the product is first processed further. They are often linked, combined, and analyzed with other data via cloud platforms. In this way, „smart data” is created – processed, intelligent data – from which knowledge can be generated. This is then the basis for tailor-made services.
Criteria for Smart Services
In Smart Services, the Big Data of the networked devices are ultimately refined into Smart Data and monetized in new, individually combinable Smart Services. The well-known pioneer for this “data refinement” is Google. Google algorithms analyze the behavior of large groups of users on different websites and their content to improve the positioning of search results. This is combined with specific data on individual Internet users for an even higher quality of search results.
Smart Services should meet three criteria in particular
- Firstly, it is necessary to ensure a connection to the Smart Product or the installed base of machines and systems for transmitting data.
- Secondly, the service provider must have the ability to interpret the data collected, i. e. it must understand the customer and the customer’s business. This is the only way to turn collected data into valuable information and useful offers.
- Finally, the service provider must also react appropriately to the generated information and achieve a beneficial effect for the customer, for example by proactively initiating the maintenance of the Smart Product.
Some examples of Smart Services
With Smart Services, companies can offer their customers added value beyond the actual product benefits. These additional data transmission services – Value Added Services – are no longer limited to the actual products, but rather exceed and often separate from them.
Simple Smart Services and business models based on them are already in use. This includes, for example, tracking packages with a smartphone app, booking a nearby car or displaying the currently cheapest connection in public transport. These services become more attractive and user-friendly the more a comprehensive network between them takes place.
In the health care sector, a Smart Service can help to improve the quality of treatment by transferring patient data to the attending physicians. Agricultural machines equipped with sensors collect information and can be combined with topology data and weather forecasts, allowing optimal fertilization and harvesting strategies.
The most important areas of application
3D printing is a prime example of smart services. 3D printing makes development and production more flexible and individualized. The article “Smart Services: Business Model Innovations through 3D Printing” in the magazine’ Wirtschaftsinformatik & Management’ reads: “Integration in Smart Services can shift and revolutionize the established value creation of product-related services”.
If the areas of application are systematized, the following areas in which Smart Services can be used are currently the main ones:
- Personal digital services, such as the measurement of sporting performance or health status (quantified self).
- Digital services in the context of home automation, e. g. for monitoring and controlling consumer electronics, energy consumption and security (keyword: Smart Home).
- Digital supported public, municipal and administrative services in urban areas (keyword: Smart City).
- Logistics and mobility services and their intelligent and multimodal networking (keyword: Smart Mobility).
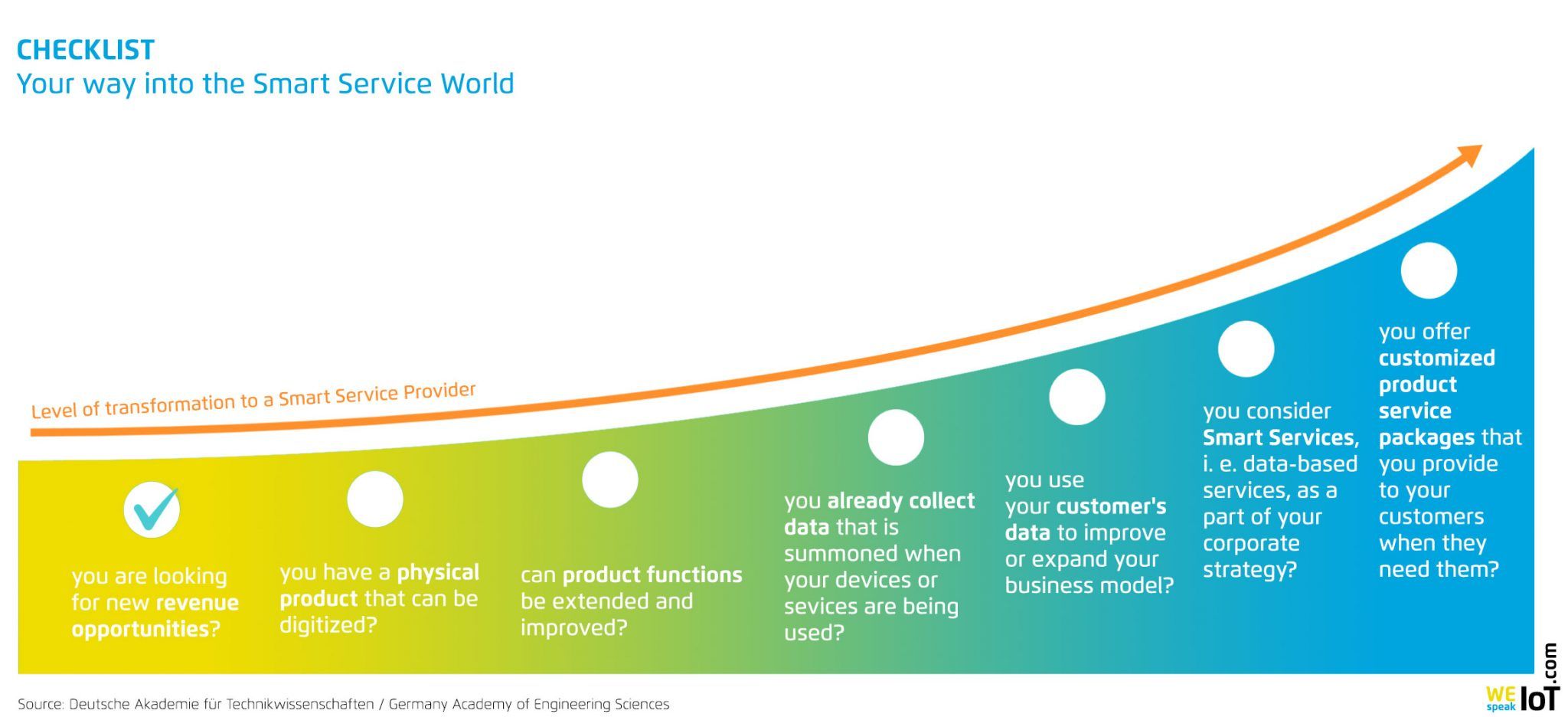
The different degrees of transformation on the way to the Smart Service Business Model.
Towards the Smart Service Business Model
How to make the leap to a Smart Service business model? Changing from product-centered to user-centered business models requires a rethink. Because the focus is no longer on products but on services, a smart service provider needs a comprehensive understanding of the user, his or her behavior and demands. This includes the courage to engage in disruption: it is about questioning traditions, developing a “different way of thinking” and changing perspectives. The tried and tested must be questioned and new structures introduced step by step.
Specifically, this means that the existing business model should be fundamentally realigned: a company should try to take away the focus from the manufacture and sale of products and try to design a service based on it. The aim should be a new, digital business model that complements the existing business model in the medium term and even replaces or refines it in the long term.
To avoid entry barriers (“start small”), data-based business models can initially be tested on a small scale. Afterwards, the business model must be rapidly developed and expanded in order to achieve the scalability that is urgently needed for Smart Services (“scale fast”). It can be useful for resource-poor, small companies to integrate into existing Smart Service systems.